ASP.NET Core 極簡風 - Minimal API
| | | 5 | |
先前展示過用 50 行 Program.cs 寫個 ASP.NET Core CORS 上傳服務,從讀者 Joker 留言我學到新名詞 - Minimal API,身為極簡主義者,它絕對是我的菜,特整理一篇備忘。
對於 Minimal API,官方文件有篇完整介紹 - Minimal APIs overview,這篇是我自己的摘要與整理,方便未來施工參考。
基本應用
首先,ASP.NET Core 從 6.0 開始引進 Minimal API,配合 Top-Level Statements,當使用 dotnet new web 建立一個空白網站時,整個專案程式部分只有一個 Program.cs,而且只有四行:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.Run();
但這樣就夠跑出一個 Hello World! 超迷你網站了。
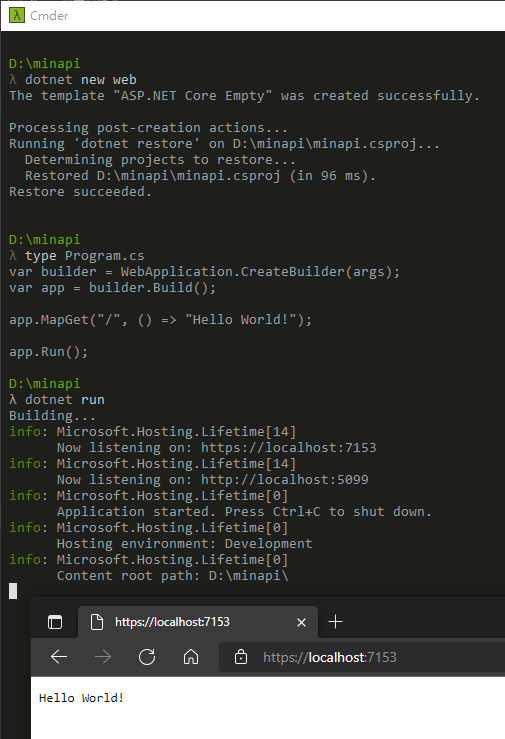
dotnet new web 所建立的空白網站專案使用 WebApplicationBuilder 建立網站,它會自動依 Properties/launchSettings.json 設定同時開放 http: 及 https: 存取。我們也可透過 app.Run("http://localhost:3000") 或 app.Urls.Add("http://localhost:3000") 指定 URL,但實務上通常不會寫死在程式裡,透過 dotnet run --urls="http://lcoalhost:3000" 或指定 ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://localhost:3000 環境變數,或是由 appsettings.json 設定檔指定是較常見的做法。
SSL 憑證
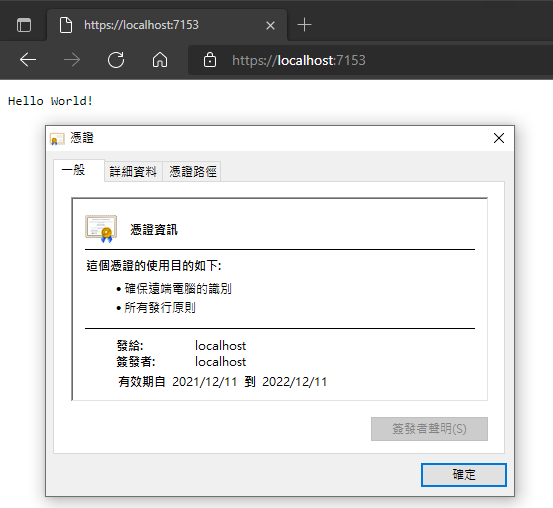
當網站啟用 HTTPS 時,ASP.NET Core 預設會產生並使用開發測試專用自簽憑證:
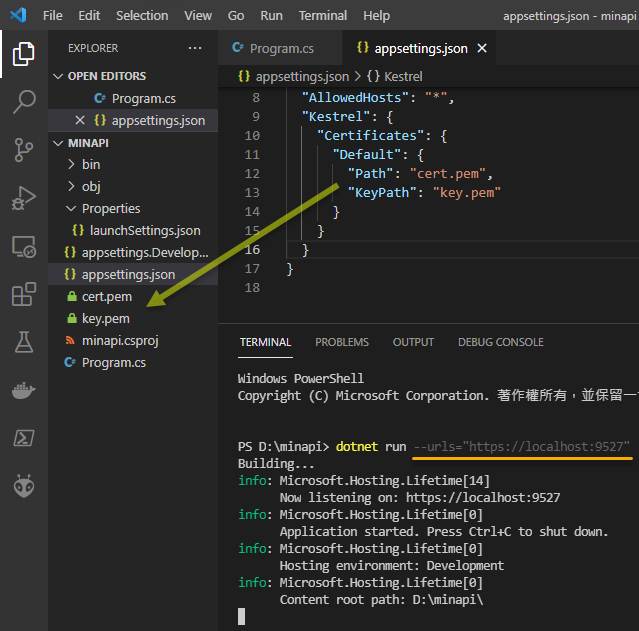
若要換成其他憑證,可修改 appsettings.json 指定憑證及私鑰檔案(註:用 OpenSSL 自建 CA 及發憑證方法可參考:使用 OpenSSL 製作 SSL 憑證):(順便示範用 --urls 參數指定網端傾聽網址)
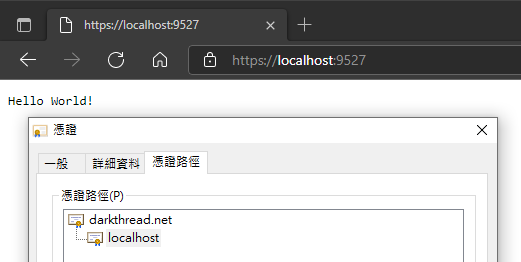
如此,ASP.NET Core 網站即會改用指定的憑證。
DI 與服務
另外,ASP.NET Core 6.0 省略 Startup.cs 又大幅簡化了 Program.cs,不再有 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)、public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env),不就無法用依賴注入存取 IConfiguration、IWebHostEnvironment、ILoggerFactory ?(延伸閱讀:不可不知的 ASP.NET Core 依賴注入
一開始接觸 ASP.NET Core 6 我有點不知所措,後來知道 ASP.NET Core 把它們都掛在 WebApplication 物件下:
- app.Configuration --> IConfiguration
- app.Environment --> IWebHostEnvironment
- app.Logger --> ILogger
至於原本寫在 ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) 的服務註冊,則要改用 builder.Services,例如:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddScoped<SampleService>();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapControllers();
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var sampleService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<SampleService>();
sampleService.DoSomething();
}
app.Run();
除了基本功能,WebApplication 也可以加掛各式各樣的 Middleware,像是 app.UseFileServer() 後,網站便能提供 .html、.css、.js 及圖檔存取,另外像是帳號登入、CORS、Response Cache、WebSocket... 等,都可視需要加掛。
處理請求
直接用範例說明常用的請求處理規則、路由設定及參數取得:
// 同一網址依 HTTP Method 決定處理邏輯
app.MapGet("/", () => "This is a GET");
app.MapPost("/", () => "This is a POST");
app.MapPut("/", () => "This is a PUT");
app.MapDelete("/", () => "This is a DELETE");
// 可一次對映多個 HTTP Method
app.MapMethods("/options-or-head", new[] { "OPTIONS", "HEAD" },
() => "This is an options or head request ");
// 由 URL 路徑取得參數
app.MapGet("/users/{userId}/books/{bookId}",
(int userId, int bookId) => $"The user id is {userId} and book id is {bookId}");
// 萬用字元 * 將後方部分視為一個參數
app.MapGet("/posts/{*rest}", (string rest) => $"Routing to {rest}");
// 加上參數型別限制
app.MapGet("/todos/{id:int}", (int id) => db.Todos.Find(id));
app.MapGet("/todos/{text}", (string text) => db.Todos.Where(t => t.Text.Contains(text));
app.MapGet("/posts/{slug:regex(^[a-z0-9_-]+$)}", (string slug) => $"Post {slug}");
除了透過路由取值,ASP.NET Core 也會自動繫結從 QueryString、Header、Body(JSON 格式)、DI 送來的參數(注意:.NET 6 未內建支援繫結 Form 送出內容),例如:
// id 來自 URL 路徑、page 來自 QueryString 或 Header,service 則來自依賴注入
app.MapGet("/{id}", (int id, int page, ISomeService service) => { });
// person 來自 Body JSON
app.MapPost("/", (Person person) => { });
// 明確指定參數來源
app.MapGet("/{id}", ([FromRoute] int id,
[FromQuery(Name = "p")] int page,
[FromServices] Service service,
[FromHeader(Name = "Content-Type")] string contentType)
=> {});
// 參數預設為必要,選擇性參數需額外註明
app.MapGet("/list1", (int? pageNumber) => $"Requesting page {pageNumber ?? 1}");
app.MapGet("/list2", (int pageNumber = 1) => $"Requesting page {pageNumber}");
若繫結邏輯複雜,還有兩種客製化繫結的方法:1. 型別提供 TryParse() API (可用擴充方法為現有型別加上 TryParse()) 2. 自訂 BindAsync() API。
處理回應
以上範例都是傳回字串作為網頁回應,若程式邏輯較複雜需要操作 HttpRequest、HttpResponse,語法如下:
app.MapGet("/a", (HttpContext context) => context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World"));
app.MapGet("/b", (HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) =>
response.WriteAsync($"Hello World {request.Query["name"]}"));
app.MapGet("/c", async (CancellationToken cancellationToken) =>
await MakeLongRunningRequestAsync(cancellationToken));
app.MapGet("/d", (ClaimsPrincipal user) => user.Identity.Name);
ASP.NET Core 提供了幾種回應形式:
// 字串內容
app.MapGet("/hello", () => "Hello World");
// 傳回JSON
app.MapGet("/hello", () => new { Message = "Hello World" });
// 傳回 IResult
app.MapGet("/hello", () => Results.Ok(new { Message = "Hello World" }));
// 指定 StatusCode
app.MapGet("/api/todoitems/{id}", async (int id, TodoDb db) =>
await db.Todos.FindAsync(id)
is Todo todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound())
.Produces<Todo>(StatusCodes.Status200OK) // 若為 Todo 型別傳 200
.Produces(StatusCodes.Status404NotFound);
// 傳回 JSON
app.MapGet("/hello", () => Results.Json(new { Message = "Hello World" }));
// 自訂 Status Code
app.MapGet("/405", () => Results.StatusCode(405));
// 傳純文字
app.MapGet("/text", () => Results.Text("This is some text"));
// 傳回 Stream
app.MapGet("/pokemon", async () =>
{
var stream = await proxyClient.GetStreamAsync("http://consoto/pokedex.json");
// Proxy the response as JSON
return Results.Stream(stream, "application/json");
});
// 重新導向
app.MapGet("/old-path", () => Results.Redirect("/new-path"));
// 傳回檔案
app.MapGet("/download", () => Results.File("myfile.text"));
若 ASP.NET Core 提供的回應形式不敷使用,也可以自己客製 IResult。
進階主題
還有一些較進階的應用情境,像是身分認證、CORS、OpenAPI... 這部分我應用 Miminal API 的情境不太會遇到,記下關鍵字,等遇到再學。
My notes of ASP.NET 6.0 minimal APIs.
Comments
# by Joker
被點名嚇了一跳 黑大更新速度好快!! 結尾提到的設定都跟之前寫法差不多其實。 黑大新年快樂
# by Alpha
其實第一個範例只要3行就可以了 var app = WebApplication.Create(args);
# by Nelson
使"月"開發,這裡打錯字了,應該跟我一樣是用倉頡😁
# by Jeffrey
to Nelson, 噗,滿滿的錯字已成我文章的特色了,謝謝指正。
# by sss
写得很好