前端筆記 - 瀏覽器端資料長期儲存解決方案:localStorage、IndexedDB 與 OPFS
| | | 0 | |
上回提到在瀏覽器裡跑的 SQL 引擎 - SQLite WASM 帶出 DB 檔案該存哪裡的議題,我後來用序列化存進 localStroage 做了簡單示範,但 localStorage 5 ~ 10 MB 的容量上限明顯限制了應用場景。
除了 localStorage,瀏覽器還有另外兩種長期儲存資料的好選項:IndexedDB 及 OPFS,這篇將實地操練一番,將這兩項技術正式列為未來可應用的解決方案。
先來張比較表:
| 項目 | localStorage | IndexedDB | OPFS (Origin Private File System) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 儲存容量 | 約 5-10MB(依瀏覽器不同) | 高,可用磁碟空間的 10%-60%,最高可達數 GB | 無固定初始限制,受磁碟空間和瀏覽器限制 |
| 資料類型 | 字串,需 JSON 處理物件 | 支援多種資料類型(物件、二進位、檔案等) | 主要是二進位檔案,支援檔案和目錄操作 |
| API 複雜度 | 簡單同步 API | 較複雜,非同步,需事件或 Promise 處理 | 檔案系統風格 API,直覺易懂 |
| 操作模式 | 同步操作,易阻塞主執行緒 | 非同步操作,不阻塞主執行緒 | 支援同步與非同步操作,WebWorker 可用同步存取 |
| 效能 | 低延遲,快速小量讀寫 | 良好,但寫入延遲稍高,初始化需時間 | 效能最高,較 IndexedDB 快3-4倍,適合高效能需求 |
| 安全性 | 易被存取,不適合敏感資料 | 支援交易,資料一致性較佳 | 資料對使用者不可見,提供更好隱私保護 |
| 適用情境 | 小型資料,使用者偏好設定,表單暫存 | 大量結構化資料,適合 PWA 離線應用,複雜查詢 | 高速檔案操作,媒體處理,大型檔案分塊上傳 |
但要注意,以上三者都會因為使用者清除瀏覽器記錄而消失,使用無痕模式時無法讀取及長期保存。考慮前述特性,這些儲存只適合用來存快取、暫存性質,或遺失不會心痛的資料,重要資料還是要存回伺服器端。
不囉嗦直接上程式碼。
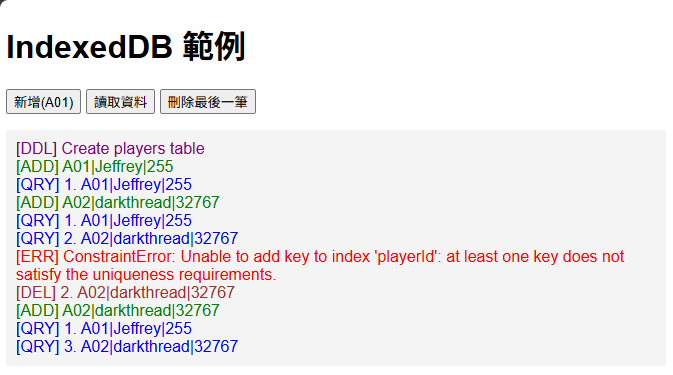
MDN 的 IndexedDB 說明文件是最好的參考來源﹐它的操作方式有點特殊,建立 IDBRequest 透過 onupgradeneeded 事件建立資料庫,IDBTransaction 物件再透過 onsuccess 事件取得查詢結果、oncomplete 事件確認動作完,錯誤處置則是靠 onerror,走一個非同步路線。我寫了一個簡單的範例包含新增、刪除、讀取,補充說明寫在註解。線上展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-tw">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>IndexedDB 範例</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 6px;
}
ul {
width: 640px;
min-height: 100px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
padding: 10px;
li {
list-style-type: none;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>IndexedDB 範例</h1>
<button onclick="testAdd()">新增<span id="currPlayerId"></span></button>
<button onclick="testRead()">讀取資料</button>
<button onclick="testDel()">刪除最後一筆</button>
<ul id="output"></ul>
<script>
const output = document.getElementById('output');
const colorMapping = {
'ERR': 'red',
'QRY': 'blue',
'ADD': 'green',
'DEL': 'brown',
'DDL': 'purple'
};
function log(action, message) {
const li = document.createElement('li');
li.textContent = `[${action}] ${message}`;
li.style.color = colorMapping[action] || 'black';
output.appendChild(li);
}
class player {
constructor(playerId, name, score) {
this.playerId = playerId;
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
static display(playerObj) {
return `${playerObj.playerId}|${playerObj.name}|${playerObj.score}`;
}
}
const sampleData = [
new player('A01', 'Jeffrey', 255),
new player('A02', 'darkthread', 32767)
];
let sampleIndex = 0;
function updatePlayerId() {
document.getElementById('currPlayerId').textContent = `(${sampleData[sampleIndex].playerId})`;
}
updatePlayerId();
let db;
// 開啟或建立資料庫
// 如果要異動資料庫結構,可指定不同的版本號
// 在 onupgradeneeded 事件變更資料庫結構
const request = indexedDB.open('MyTestDB', 1);
// 新建或升級資料庫時會觸發 onupgradeneeded 事件
request.onupgradeneeded = function (event) {
db = event.target.result;
if (!db.objectStoreNames.contains('players')) {
const dbStore = db.createObjectStore('players', { keyPath: 'id', autoIncrement: true });
// 可建立索引限制重複資料或加速查詢
dbStore.createIndex('playerId', 'playerId', { unique: true });
dbStore.createIndex('name', 'name', { unique: false });
log('DDL', 'Create players table');
}
};
// 開啟資料庫的成功失敗事件
request.onsuccess = function (event) {
db = event.target.result;
};
request.onerror = function (event) {
log('ERR', event.target.errorCode);
};
function testAdd() {
const tx = db.transaction('players', 'readwrite');
const store = tx.objectStore('players');
const addRequest = store.add(sampleData[sampleIndex]);
const userDisplay = player.display(sampleData[sampleIndex]);
addRequest.onerror = function (event) {
log('ERR', event.target.error);
};
sampleIndex = (sampleIndex + 1) % sampleData.length; // 循環使用範例資料
updatePlayerId();
tx.oncomplete = function () {
log(`ADD`, userDisplay);
};
};
function testDel() {
const tx = db.transaction('players', 'readwrite');
const store = tx.objectStore('players');
const request = store.getAll();
request.onsuccess = function () {
const results = request.result;
if (results.length > 0) {
const lastItem = results[results.length - 1];
const deleteRequest = store.delete(lastItem.id);
deleteRequest.onsuccess = function () {
log(`DEL`, lastItem.id + '. ' + player.display(lastItem));
};
} else {
log('QRY','No items to delete.');
}
};
};
function testRead() {
const tx = db.transaction('players', 'readonly');
const store = tx.objectStore('players');
const request = store.getAll();
request.onsuccess = function () {
const results = request.result;
results.forEach(item => {
log(`QRY`, `${item.id}. ${player.display(item)}`);
});
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
要更新則是利用 store.put():
function testUpdate() {
const tx = db.transaction('players', 'readwrite');
const store = tx.objectStore('players');
// 修改現有資料
const updatedPlayer = new player('A01', 'Jeffrey Updated', 9999);
updatedPlayer.id = 1; // 需要指定主鍵 id
const updateRequest = store.put(updatedPlayer);
updateRequest.onsuccess = function() {
log('UPD', `Updated: ${player.display(updatedPlayer)}`);
};
updateRequest.onerror = function(event) {
log('ERR', event.target.error.message);
};
}
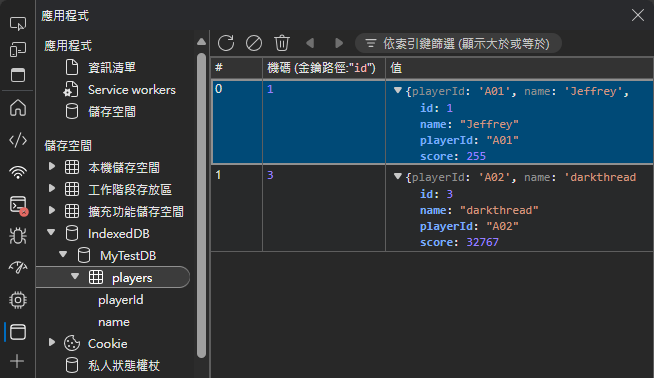
F12 開發者工具有 IndexedDB 資料檢視器,挺方便的。
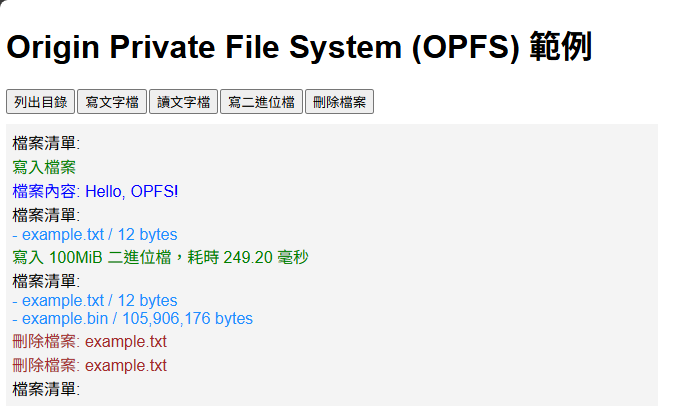
至於 OPFS(Origin Private File System),一樣可以參考 MDN 文件,OPFS 的 API 用起來蠻直覺,基本上就像操作一般的檔案系統,而且直接支援 async/await 要同步或非同步處理都很方便。我實測用 OPFS 寫入 100MB 檔案只需 0.25 秒,效率很不錯,加上可在 Web Worker 使用,非常適用來處理大型資料。線上展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>OPFS Example</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.prod.js"></script>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 6px;
}
button {
margin-right: 2px;
}
.messages {
width: 640px;
margin-top: 10px;
min-height: 100px;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
padding: 6px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>Origin Private File System (OPFS) 範例</h1>
<button @click="listRootDirectory">列出目錄</button>
<button @click="writeFile">寫文字檔</button>
<button @click="readFile">讀文字檔</button>
<button @click="writeBinaryFile">寫二進位檔</button>
<button @click="deleteFiles">刪除檔案</button>
<div class="messages">
<div v-for="log in logs" :key="log.id" :style="{ color: log.color }">
{{ log.message }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const { createApp } = Vue;
createApp({
data() {
return {
fileName: 'example.txt',
logs: []
}
},
methods: {
log(message, color = 'black') {
this.logs.push({ id: Date.now(), message, color });
},
async getRootDir() {
if ('storage' in navigator && 'getDirectory' in navigator.storage) {
return await navigator.storage.getDirectory();
} else {
throw new Error('OPFS not supported');
}
},
async listRootDirectory() {
try {
const root = await this.getRootDir();
const entries = [];
this.log('檔案清單:');
for await (const entry of root.values()) {
const file = await entry.getFile();
this.log(` - ${entry.name} / ${file.size.toLocaleString()} bytes`, 'dodgerblue');
}
} catch (e) {
this.log(e.message, 'red');
}
},
async writeFile() {
try {
const root = await this.getRootDir();
const fileHandle = await root.getFileHandle(this.fileName, { create: true });
const writable = await fileHandle.createWritable();
await writable.write('Hello, OPFS!');
await writable.close();
this.log('寫入檔案', 'green');
} catch (e) {
this.log(e.message, 'red');
}
},
async readFile() {
try {
const root = await this.getRootDir();
const fileHandle = await root.getFileHandle(this.fileName);
const file = await fileHandle.getFile();
const text = await file.text();
this.log(`檔案內容: ${text}`, 'blue');
} catch (e) {
this.log(e.message, 'red');
}
},
async deleteFiles() {
try {
const root = await this.getRootDir();
for await (const entry of root.values()) {
await entry.remove();
this.log(`刪除檔案: ${this.fileName}`, 'brown');
}
} catch (e) {
this.log(e.message, 'red');
}
},
async writeBinaryFile() {
try {
const root = await this.getRootDir();
const fileHandle = await root.getFileHandle('example.bin', { create: true });
const writable = await fileHandle.createWritable();
const chunkSize = 1024 * 1024; // 1MB
const totalSize = 100 * 1024 * 1024; // 100MB
const buffer = new Uint8Array(chunkSize).fill(0xAB); // 模擬資料
const start = performance.now();
for (let written = 0; written < totalSize; written += chunkSize) {
await writable.write(buffer);
}
await writable.write(buffer);
await writable.close();
const end = performance.now();
this.log(`寫入 ${totalSize / 1024 / 1024}MiB 二進位檔,耗時 ${(end - start).toFixed(2)} 毫秒`, 'green');
} catch (e) {
this.log(e.message, 'red');
}
}
}
}).mount('#app');
</script>
</body>
</html>
當然,OPFS 也支援子資料夾結構,列舉項目時,可由 kind == 'file' 或 'directory' 判斷是目錄還是檔案:
async function opfsWriteReadExample() {
try {
// 取得 OPFS 根目錄
const opfsRoot = await navigator.storage.getDirectory();
// 建立子資料夾 mainFolder
const mainFolderHandle = await opfsRoot.getDirectoryHandle('mainFolder', { create: true });
// 在 mainFolderHandle 裡建立檔案 example.txt
const fileHandle = await mainFolderHandle.getFileHandle('example.txt', { create: true });
// 寫入檔案內容
const writable = await fileHandle.createWritable();
await writable.write('Hello, World!');
await writable.close();
// 在 mainFolder 裡建立子資料夾 subFolder
const subFolderHandle = await mainFolderHandle.getDirectoryHandle('subFolder', { create: true });
// 列舉 mainFolder 裡的檔案和資料夾
console.log('mainFolder 內容:');
for await (const entry of mainFolderHandle.values()) {
console.log(` - ${entry.name} (${entry.kind})`);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('OPFS 操作錯誤:', error);
}
}
// 執行範例
opfsWriteReadExample();
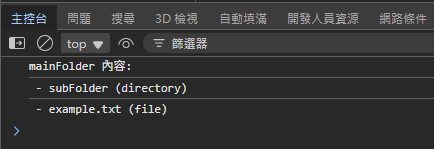
F12 開發者工具僅能觀察 OPFS 佔用的空間,沒有內建檔案總管之類的檢視工具,如有需求可使用第三方外掛或寫幾行程式搞定。
至此,對 IndexedDB 與 OPFS 就算有了基本認識囉~
This post explores long-term data storage options in browsers: IndexedDB and OPFS. IndexedDB offers structured data storage with asynchronous API, while OPFS provides high-performance file system-like operations, ideal for large files. Both are suitable for caching and temporary storage due to their persistence limitations.
Comments
Be the first to post a comment