用 100 行 C# 打造 IP 所屬國家快速查詢功能
 |  | 6 |  |  |
講到由 IP 地址查詢所屬國家,解決方案有兩種:第一種是直接呼叫線上查詢 API(付費或免費),再不然就要下載 IP 區段資料庫自寫查詢程式。考量應用場合不一定有 Internet 連線能力,加上擔心線上 API 無法滿足 IIS Log 等超大量 IP 解析的效能要求,選擇取回資料檔自幹。(其實是因為這題目大小難易適中,十分適合練功,一時手癢難耐,就…)
爬文找到一些 IP 國別對應資料來源:
- Maxmind GeoIP2 https://www.maxmind.com/en/geoip2-country-database
Maxmind 在 Stackoverflow 受到不少網友推薦。精準度高(99.8%),另有對應到城市、ISP的版本,甚至有準確率分析報告,十分專業,授權費用每個站台 $50。 - Maxmind GeoLite2 http://dev.maxmind.com/geoip/legacy/geolite/
GeoIP2 的免費版,格式較舊,精確度不如 GeoIP2,使用時需註明來源連結(CC-BY-SA 授權)。 - IPInfoDB LITE版 http://ipinfodb.com/ip_database.php
提供 CSV 資料庫下載,查詢準確率 >98%,使用時需於網站加註連結(CC-BY-SA 授權)。 - ip2c.org http://www.ip2c.org/
免費(LGPL授權)且無使用量限制的 API 服務,精準率(99.95%),GET httq://ip2c.org/XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 直接拿結果,乾淨俐落,是 API 服務的首選,但未提供資料庫下載。 - software77 http://software77.net/geo-ip/
ip2c.org 的資料來源,每 24 小時更新,有 CSV 可下載,為捐款軟體(Donationware,自由捐獻)。 - ip2nation.com http://www.ip2nation.com/ip2nation
完全免費且無限制,直接提供 MySQL Script 方便匯入資料表進行查詢,精準率約 98-99%。
最後決定選用 software77 的資料,看中它每日更新以及號稱 99.95% 的準確率。(各家資料格式大同小異,要更換來源並非難事,微調匯入邏輯即可)
由網站取回 IpToContry.csv 格式如下,前方有一大段註解直接略過即可。資料部分共有七欄,第1、2欄為 IP 區段的起始位址及結束位址(IP 位址不使用 aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd 字串格式,而是將四個 Byte 轉換為整數),第 5 欄為國別代碼,第 7 欄有國家名稱。
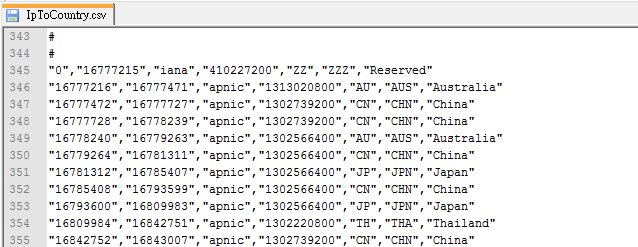
一般處理 IP 區段查詢,最常見做法是轉進資料庫後使用 SQL 查詢。評估資料筆數大約 17 萬筆,轉成物件陣列放進記憶體進行查詢對 C# 及當代電腦硬體是一碟小菜,不依賴資料庫的輕巧小程式更貼近我的開發哲學,用一個小類別打死才帥。
先不費太多腦力,用最直覺的 C# LINQ 來解:定義一個範圍物件 IPRange,屬性包含起始位址、結束位址、國別代碼、國家名稱。將資料檔轉為 List<IPRange>,查詢用 .SingleOrDefault(o => ip >= o.Start && ip <= o.End) 就能輕鬆達成, 50 行搞定:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Net; namespace IP2C.Net { public class RookieIPCountryFinder
{ public class IPRange
{ public uint Start;
public uint End;
public string CnCode;
public string CnName;
}
List<IPRange> Ranges = new List<IPRange>(); public RookieIPCountryFinder(string path)
{ foreach (var line in File.ReadAllLines(path))
{ if (line.StartsWith("#")) continue;
//"87597056","87599103","ripencc","1338422400","ES","ESP","Spain" var p = line.Split(',').Select(o => o.Trim('"')).ToArray();
Ranges.Add(new IPRange() { Start = uint.Parse(p[0]), End = uint.Parse(p[1]), CnCode = p[4],
CnName = p[6]
});
}
}
public uint GetIPAddrDec(string ipAddr)
{ byte[] b = IPAddress.Parse(ipAddr).GetAddressBytes(); Array.Reverse(b);
return BitConverter.ToUInt32(b, 0); }
public string GetCountryCode(string ipAddr)
{ uint ip = GetIPAddrDec(ipAddr); var range = Ranges.SingleOrDefault(o => ip >= o.Start && ip <= o.End);;
if (range == null)
return "--";
else return range.CnCode; }
}
}
為了驗證結果,從 https://www.randomlists.com/ip-addresses 取得 1024 筆隨機網址,以 http://www.ip2c.org/168.95.1.1 方式查出國別,做好 1024 筆測試資料。以單元測試執行批次查詢與 ip2c.org 查詢結果進行比對,驗證結果是否一致。
測試前先觀察 ip2c.org API 執行速度方便比較,經實測一次耗時約 950 – 975ms。
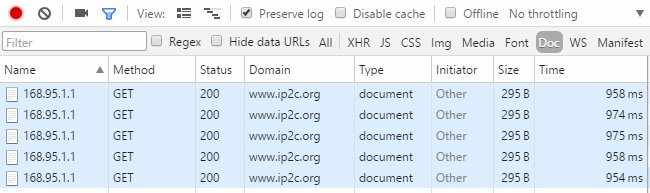
執行單元測試,隨機 1024 筆資料查詢結果與 ip2c.org 查詢結果一致(綠燈),總查詢時間約 4.5 秒,換算每次查詢約 4.5ms,比呼叫 API 快 200 倍。
不過,LINQ 查詢固然直覺方便,若你以為它會像 SQL WHERE 查詢一樣有效率就錯了,恭喜跌入效能陷阱。如果講求效能,得換一顆更專業的查詢引擎。從已排序陣列找出指定數字落點,二分搜尋法是我心中的首選,原以為得捲袖子自已寫,卻發現 Array.BinarySearch 在 .NET 已內建 ,哈里路亞!
配合二分搜尋,匯入資料結構也要調整,我的做法是將開始位址及結束位址轉成數字陣列,使用 Dictionary 對應國別碼。有個問題是範圍與範圍間可能存在未定義的空隙,發現範圍不連續時要補上一段開始、結束範圍指向未定義國別(國別碼填入"—"),才能精準回報未定義。另外,資料中有五個區段被重複定義指向兩個不同國家(實務可能發生,參見 FAQ),處理時也需排除。
查詢核心以 Array.BinarySearch 找出 IP 位址在已排序陣列的相對位置,若在陣列裡找不到該數字,BinarySearch 會傳回最接近位置的補數,轉換後可找到所屬範圍的位址。BinarySearch 版本範例如下,加上簡單的防錯,100 行搞定:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Net; using System.Text; namespace IP2C.Net { public class IPCountryFinder
{ Dictionary<string, string> CountryNames = new Dictionary<string, string>();
Dictionary<uint, string> IP2CN = new Dictionary<uint, string>();
uint[] IPRanges; public string DupDataInfo = string.Empty;
public IPCountryFinder(string path)
{ if (!File.Exists(path)) throw new ArgumentException($"{path} not found!");
string dupInfo = null;
StringBuilder dupData = new StringBuilder(); uint lastRangeEnd = 0; string unknownCode = "--";
CountryNames.Add(unknownCode, "Unknown"); int count = 0; try { foreach (var line in File.ReadAllLines(path))
{ if (line.StartsWith("#")) continue;
try { //"87597056","87599103","ripencc","1338422400","ES","ESP","Spain" var p = line.Split(',').Select(o => o.Trim('"')).ToArray();
var st = uint.Parse(p[0]); var ed = uint.Parse(p[1]); var cn = p[4];
//range gap found if (lastRangeEnd > 0 && st > lastRangeEnd) { //padding unknown range IP2CN.Add(lastRangeEnd, unknownCode);
IP2CN.Add(st - 1, unknownCode);
count += 2;
}
dupInfo = $"{st}-{ed}-{cn}"; IP2CN.Add(st, cn);
IP2CN.Add(ed, cn);
lastRangeEnd = ed + 1;
if (!CountryNames.ContainsKey(cn)) CountryNames.Add(cn, p[6]);
}
catch (ArgumentException aex) { dupData.AppendLine($"Duplicated {dupInfo}: {aex.Message}"); }
}
IPRanges = IP2CN.Select(o => o.Key).OrderBy(o => o).ToArray();
}
catch (Exception ex) { throw new ApplicationException($"CSV parsing error: {ex.Message}");
}
DupDataInfo = dupData.ToString();
}
public uint GetIPAddrDec(string ipAddr)
{ byte[] b = IPAddress.Parse(ipAddr).GetAddressBytes(); Array.Reverse(b);
return BitConverter.ToUInt32(b, 0); }
public string GetCountryCode(string ipAddr)
{ uint ip = GetIPAddrDec(ipAddr); int idx = Array.BinarySearch(IPRanges, ip); if (idx < 0) { int idxNearest = ~idx; if (idxNearest > 0) idxNearest--; idx = idxNearest;
}
return IP2CN[IPRanges[idx]]; }
public string ConvertCountryCodeToName(string cnCode)
{ if (CountryNames.ContainsKey(cnCode)) return CountryNames[cnCode]; return cnCode; }
public string GetCountryName(string ipAddr)
{ return ConvertCountryCodeToName(GetCountryCode(ipAddr)); }
}
}
以相同資料重新測試 BinarySearch 引擎版本。
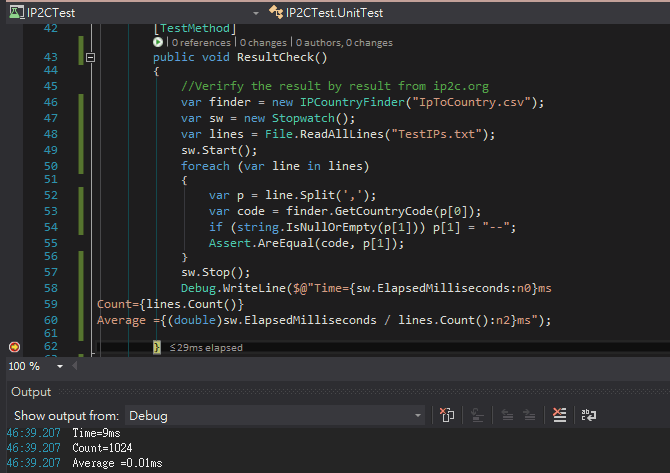
薑!薑!薑!薑~ 1024 筆只花了 9ms!!平均每一筆耗時 0.01 ms,比 LINQ 查詢版快了450 倍,比呼叫 API 快了 9 萬倍!速度快到嚇我一大跳,雖然大部分是 Array.BinarySearch 的功勞,但我很滿意。

完整程式及單元測試已放上 Github,有興趣玩玩的同學請自取。
呼口號時間:
Comments
# by Joney
請問 if (idxNearest > 0) idxNearest--; 這行是取st位置的index, 且順便解決Array的max index + 1這個問題嗎??
# by Jeffrey
to Joney, 依據MSDN文件:https://goo.gl/b97Hty If the Array does not contain the specified value, the method returns a negative integer. You can apply the bitwise complement operator (~ in C#, Not in Visual Basic) to the negative result to produce an index. If this index is one greater than the upper bound of the array, there are no elements larger than value in the array. Otherwise, it is the index of ** the first element that is larger than value **. 負數取補數得到的是第一個大於該值的元素索引,依我的理解較像 ed, 減 1 相當於 st 位置,二者指向相同國別,結果不變;當輸入位址超出範圍上限時(目前CSV定義到255.255.255.255,不致發生),會傳回 Ranges.Length,減1可避免索引超出限制出錯。
# by Joney
to Jeffrey, 我是在同一個MSDN看到Return Value的定義 Type: System.Int32 The index of the specified value in the specified array, if value is found; otherwise, a negative number. If value is not found and value is less than one or more elements in array, the negative number returned is the bitwise complement of the index of the first element that is larger than value. If value is not found and value is greater than all elements in array, the negative number returned is the bitwise complement of (the index of the last element plus 1). If this method is called with a non-sorted array, the return value can be incorrect and a negative number could be returned, even if value is present in array. 想釐清我是否理解錯誤, 配合您的解說, 看來我沒理解錯誤, 感謝您的釋疑~~
# by lisa
請問如果是ipv6 十進位最高到39位數,該怎麼處理?
# by Jeffrey
to lisa, 排序與搜尋原理相同,但IPv6有128bit,long(64bit)也裝不下,需動用BigInteger( https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-tw/library/system.numerics.biginteger(v=vs.110).aspx )或自訂型別記錄及運算,資料空間較大,執行速度較慢,但此做法仍應可行。
# by Polly
I saw you use ipinfodb, Maxmind and ip2c etc. I thought you might like to know about our service at https://ipinfo.io. Our geolocation API is free for up to 1,000 req/day, and includes hostname and ASN details too.